While starting to work and exercise with ZFS filesystem, a newbie will face a lot of new terminology: most of these keywords, naturally, you never heard of.
Not only the terminology but the system administration skills and attitudes, are a lot different; sometimes you could feel a strange sense of confusion while you're approaching to this all-new mindset you are required to adopt to acocmplish your new mission: understanding how ZFS works.
This is a brief description of the terminology relative to ZFS:
- alternate boot environment
-
A boot environment that is created by the lucreate command and possibly updated by the luupgrade command, but it is not the active or primary boot environment. The alternate boot environment can become the primary boot environment by running the luactivate command.
- checksum
-
A 256-bit hash of the data in a file system block. The checksum capability can range from the simple and fast fletcher4 (the default) to cryptographically strong hashes such as SHA256.
- clone
-
A file system whose initial contents are identical to the contents of a snapshot.
- dataset
-
A generic name for the following ZFS components: clones, file systems, snapshots, and volumes.
Each dataset is identified by a unique name in the ZFS namespace. Datasets are identified using the following format:
pool/path[@snapshot]
- pool
-
Identifies the name of the storage pool that contains the dataset
- path
-
Is a slash-delimited path name for the dataset component
- snapshot
-
Is an optional component that identifies a snapshot of a dataset
- file system
-
A ZFS dataset of type filesystem that is mounted within the standard system namespace and behaves like other file systems.
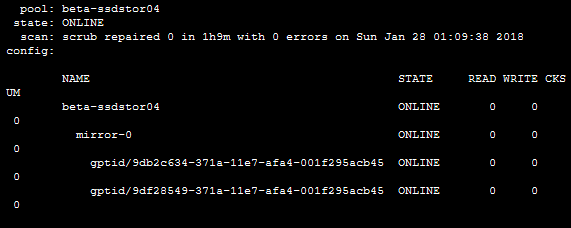
- mirror
-
A virtual device that stores identical copies of data on two or more disks. If any disk in a mirror fails, any other disk in that mirror can provide the same data.
- pool
-
A logical group of devices describing the layout and physical characteristics of the available storage. Disk space for datasets is allocated from a pool.
- primary boot environment
-
A boot environment that is used by the lucreate command to build the alternate boot environment. By default, the primary boot environment is the current boot environment. This default can be overridden by using the lucreate -s option.
- RAID-Z
-
A virtual device that stores data and parity on multiple disks.
- resilvering
-
The process of copying data from one device to another device is known as resilvering. For example, if a mirror device is replaced or taken offline, the data from an up-to-date mirror device is copied to the newly restored mirror device. This process is referred to as mirror resynchronization in traditional volume management products.
- snapshot
-
A read-only copy of a file system or volume at a given point in time.
- virtual device
-
A logical device in a pool, which can be a physical device, a file, or a collection of devices.
- volume
-
A dataset that represents a block device. For example, you can create a ZFS volume as a swap device.